Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is a Dental Bridge and Why Might You Need One?

A dental bridge, sometimes referred to as a tooth bridge, mouth bridge, or oral bridge, is a common restorative dentistry solution used to replace one or more missing teeth. This fixed appliance quite literally bridges the gap created by missing teeth by anchoring a false tooth (or teeth) — known as a pontic — between two abutment teeth on either side of the gap. These abutment teeth are typically fitted with dental crowns that support the pontic, restoring function and appearance to your smile.
Also known as dental bridging or dentistry bridgework, this treatment is ideal for people who are missing teeth but still have strong, healthy teeth on either side of the space. These supporting teeth act as the foundation for the bridge, helping to keep everything stable.
But what is a bridge in dental terms, really? In essence, it’s a fixed dental restoration — unlike dentures, which are removable. A dental bridge becomes a part of your mouth structure, providing a seamless look and feel. This makes it especially beneficial for front teeth or bridges for teeth that are visible when smiling.
Why do I need a dental bridge?
- A bridge for teeth isn’t just about cosmetics. It restores essential functions like chewing and speaking that may be affected by missing teeth.
- A gap in your teeth can cause the surrounding teeth to shift out of position over time, which can lead to bite misalignment and future oral health issues.
- Dental bridges can also help maintain the shape of your mouth and support your facial structure — preventing the sunken look that often occurs when teeth are missing.
- They can improve confidence and self-esteem by eliminating visible gaps and restoring a natural-looking smile.
Who needs a dental bridge?
- Patients who have lost one or more teeth but still have healthy, stable teeth on either side of the gap.
- People who want a fixed solution as opposed to removable dentures.
- Those who aren’t candidates for dental implants, due to health, cost, or insufficient jawbone structure.
What Are the Types of Dental Bridges and How Do They Differ?
There are several types of dental bridges, and choosing the right one depends on your specific needs, the health of your remaining teeth, and how many teeth need replacing. Each type of dental bridge is designed for different situations, offering varying levels of support and permanence.
What is a traditional dental bridge?
- A traditional dental bridge is the most common type, often recommended for people with healthy teeth on both sides of the missing gap.
- This bridge typically consists of two dental crowns placed on the teeth adjacent to the gap, and a pontic (false tooth) in between. The crowns provide the support necessary to hold the pontic in place.
- Materials used in traditional bridges include porcelain fused to metal or ceramic, which are durable and natural-looking, making them ideal for both front and back teeth.
- Advantages: Strong, durable, and effective for a wide range of patients.
What is a Maryland dental bridge?
- The Maryland dental bridge, also known as a resin-bonded bridge, uses a metal or porcelain framework that is bonded to the back of the adjacent teeth. Unlike traditional bridges, the Maryland bridge doesn’t require crowns on the abutment teeth but rather attaches using metal or porcelain “wings” that are bonded to the natural teeth.
- Ideal Use: This bridge is best suited for replacing front teeth where the aesthetic appeal is important. It’s typically used when minimal tooth preparation is preferred.
- Advantages: Less invasive, no reshaping of the surrounding teeth is necessary, and it’s more affordable than a traditional bridge.
- Disadvantages: Less durable than traditional bridges, and it may not be suitable for back teeth or for patients who need more stability.
What is a cantilever dental bridge?
- A cantilever dental bridge is used when there is only one healthy tooth available to support the bridge. Instead of being anchored on both sides, the bridge is supported on just one side, making it ideal for gaps at the back of the mouth or for situations where only one adjacent tooth remains.
- Concerns: Due to the single support, there is a higher risk of placing too much force on the remaining tooth, potentially leading to damage.
- Ideal Use: Best for smaller gaps with healthy teeth on only one side of the gap.
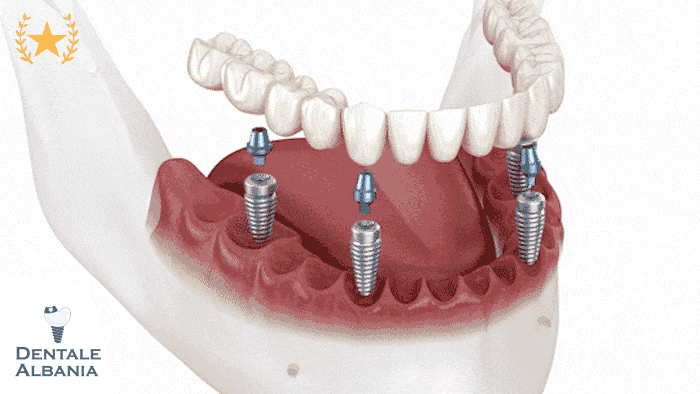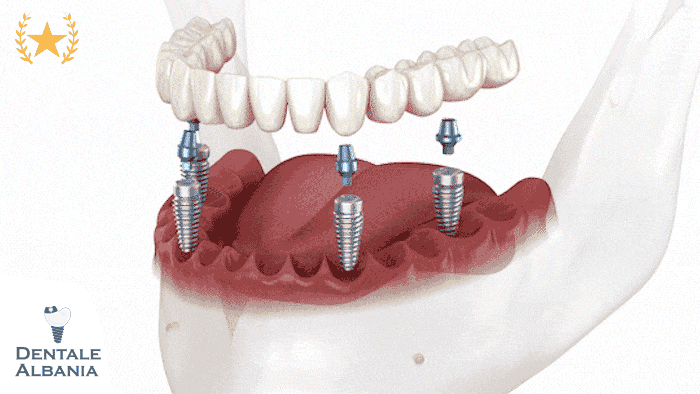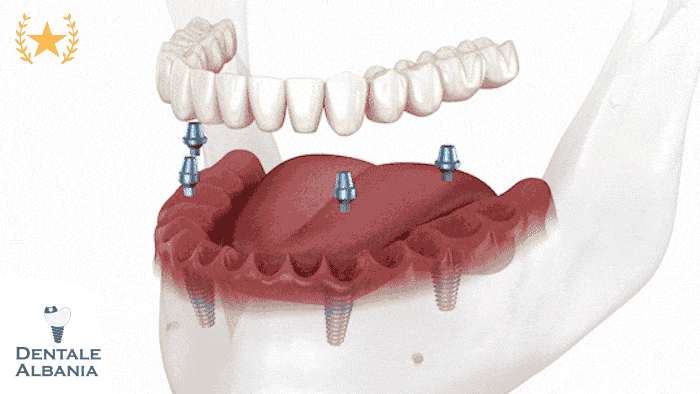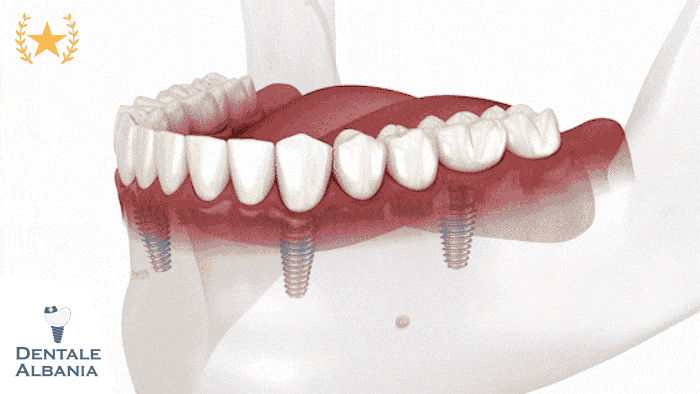
What is an implant-supported dental bridge?
- The implant-supported dental bridge is a more advanced solution, where the bridge is held in place by dental implants instead of natural teeth. This type of bridge is ideal for patients who have multiple missing teeth and cannot rely on the surrounding teeth for support.
- Procedure: Involves placing a dental implant into the jawbone to act as the anchor. After the implant integrates with the bone, the bridge is attached to it.
- Advantages: More durable, preserves the jawbone, and provides a more permanent solution.
- Disadvantages: Requires surgery, a longer healing period, and is generally more expensive.
What’s the difference between bridges and implants?
- Dental bridges are used to fill gaps by attaching false teeth to adjacent healthy teeth or dental implants. They provide support, but the surrounding teeth may need to be reshaped for the crowns.
- Dental implants, on the other hand, replace the entire tooth, including the root, by inserting a titanium post into the jawbone. Implants provide greater stability and long-term benefits, particularly for jawbone preservation.
- Key Differences:
- Longevity: Implants last longer and help preserve the jawbone, while bridges may require replacement after 5-15 years.
- Invasiveness: Implants involve surgery and a healing process, while bridges are typically faster to place.
- Aesthetic: Both offer natural-looking results, but implants may offer more precision and stability.
What Happens During a Dental Bridge Procedure?
The process of getting a dental bridge involves multiple steps, each designed to ensure that the bridge fits securely and functions as expected. The procedure typically takes place over the course of two or more dental visits. Here’s a breakdown of what you can expect during each phase of the process.
Can I Have a Bridge Fitted Straight After a Tooth Extraction?
- No, healing time is required: After a tooth extraction, it’s necessary to wait until the gum tissue has healed before placing a dental bridge. This typically takes several weeks or even months.
- Temporary solutions: During the healing period, patients may be fitted with temporary bridges or partial dentures to restore the appearance and function of the missing tooth.
- Why the wait is important: Immediate placement of a bridge after extraction could compromise the healing process, leading to complications or a poor fit for the permanent bridge later.
How Many Teeth Can Be Replaced With a Bridge?
- Number of missing teeth: A dental bridge can replace one to four missing teeth, depending on the health of the remaining teeth and the amount of bone available for support.
- Abutment teeth: The number of teeth that can be replaced often depends on the strength of the abutment teeth (the teeth on either side of the gap). These teeth must be healthy and strong enough to support the bridge.
- Longer bridges: If multiple teeth are missing, longer bridges can be used, but they might require additional support from implants for better stability.
How Long Should I Wait Before Getting a Dental Bridge?
- Healing after extraction: It’s recommended to wait until your gums and tissues have fully healed before proceeding with a dental bridge. Typically, this could take several weeks to a few months.
- Delaying placement: Waiting too long may lead to the shifting of adjacent teeth or bone loss, which can make it harder to place a bridge successfully.
- Optimal timing: Ideally, the placement of the dental bridge should occur after full gum and tissue healing to ensure the best fit and longevity.
How Much Does a Dental Bridge Cost and What Affects It?

The cost of a dental bridge can vary greatly depending on several factors. It’s essential to understand the different elements that contribute to the overall cost, especially when considering the investment for a functional, long-lasting solution to missing teeth.
What Is the Cost of a Dental Bridge in the UK?
- Private costs: The price for a dental bridge in the UK varies depending on the type of bridge and the materials used. On average, you can expect to pay anywhere between £695 to £2,500 per unit.
- NHS costs: For those seeking treatment under the NHS, the cost for a dental bridge is typically Band 3 pricing, which as of 2025 is around £282.80. However, this price is limited to specific types of bridges and may not include all options for materials or private dental consultations.
- Additional services: Depending on the treatment plan, X-rays, consultation fees, or other necessary procedures may also contribute to the total cost.
What Is the Cost of a Dental Bridge in Albania?
The cost of a dental bridge in Albania can vary depending on several factors, including the type of bridge, the materials used, and the specific dental clinic. However, compared to other countries, Albania offers affordable dental care without compromising quality, making it a popular destination for dental tourism.
What Factors Affect the Cost of a Dental Bridge?
Several factors influence the price of a dental bridge in Albania:
Type of Dental Bridge: The cost will differ depending on the type of bridge you choose:
Traditional Bridges: Typically more affordable, especially for cases where you have healthy teeth on both sides of the gap.
Maryland Bridges: Generally a more cost-effective solution for front teeth with a lower risk of damage.
Cantilever Bridges: Typically used for gaps with only one adjacent tooth, which might be less expensive than traditional bridges.
Implant-Supported Bridges: These are the most expensive option, as they require dental implants, which involve surgery and a longer recovery time.
Material Used: The choice of materials significantly affects the cost. For example, a porcelain bridge fused with metal might be more affordable than a fully ceramic or zirconia bridge, which is often chosen for aesthetic reasons.
Dental Clinic and Location: The experience of the dentist and the clinic’s location within Albania can also impact pricing. Well-established clinics with international reputations might charge a premium for their services. However, many clinics in Albania offer high-quality treatments at a fraction of the cost found in countries like the US or the UK.
Additional Procedures: If you need any preparatory treatments, such as tooth extractions or gum therapy, these will add to the total cost of the procedure. These steps ensure that your mouth is ready for the dental bridge, ensuring a successful outcome.
Average Cost of a Dental Bridge in Albania
The cost of a dental bridge in Albania is significantly lower compared to Western Europe and North America, making it a cost-effective solution for dental care.
Traditional Bridges: Prices for traditional dental bridges in Albania generally range from €200 to €600 per unit, depending on the materials used and the complexity of the procedure.
Maryland Bridges: These typically cost between €250 and €600, offering a more affordable solution for replacing front teeth.
Implant-Supported Bridges: As these involve the additional cost of dental implants, the price for an implant-supported bridge can range from €1,000 to €2,500 per unit, which includes both the bridge and the implant.
Are There Financing Options Available for Dental Bridges in Albania?
Many dental clinics in Albania offer financing plans to help patients manage the cost of their dental treatments. These options may include:
Interest-free payment plans: Many clinics allow patients to pay for their dental bridges in installments over a set period, making it more affordable.
Discounts for multiple treatments: If you need multiple bridges or other dental procedures, some clinics offer package deals that reduce the overall cost.
Insurance: Some international dental insurance providers may offer partial reimbursement for dental bridges, especially for those traveling from countries with reciprocal healthcare agreements.
Conclusion
The cost of a dental bridge in Albania is highly affordable compared to most Western countries, making it an attractive option for dental tourism. Whether you need a traditional bridge or an implant-supported bridge, you can expect to pay significantly less for high-quality care. Always consult with a local dentist to get an accurate quote based on your specific needs.
What Factors Affect the Cost of a Dental Bridge?
- Type of bridge: The type of bridge chosen has a significant impact on the cost. For example:
- Traditional dental bridges typically cost less than implant-supported bridges.
- Maryland bridges may be slightly more affordable than cantilever or implant-supported options.
- Materials used: The material of the pontic (the false tooth) and the abutment crowns plays a big role in pricing:
- Metal-ceramic or zirconia bridges are often more expensive than basic porcelain options due to their durability and aesthetic qualities.
- Location and dentist expertise: The cost can also depend on where you live and the level of experience and specialization of the dentist. Dentists in urban centers or private practices may charge more than those in smaller areas or NHS clinics.
Can I Finance My Dental Bridge Treatment?
- 0% APR finance: Many dental practices offer financing options, allowing patients to spread the cost of their dental bridge over several months or years. Some offer 0% APR plans for interest-free payments if the balance is cleared within a specified period.
- Monthly payment plans: Flexible monthly payments can make the cost of dental bridges more affordable, with some clinics providing options that cater to various budget sizes.
- Dental insurance: It’s also worth checking if your dental insurance plan offers reimbursement for part of the procedure, as some plans cover the cost of bridges, especially if they are considered medically necessary.
How Do You Care for a Dental Bridge and How Long Does It Last?
Caring for your dental bridge properly can significantly extend its lifespan, ensuring that it remains functional and aesthetically pleasing for years to come. Regular maintenance and good oral hygiene practices are essential for preventing common issues such as decay, gum disease, and bridge loosening.
How Should I Care for My Dental Bridge?
- Daily flossing: It’s crucial to floss around the pontic (the false tooth) using superfloss or floss threaders. This will help clean the space under the bridge and prevent plaque buildup, which could lead to tooth decay or gum problems.
- Use interdental brushes: These brushes are designed to clean between your teeth and around your bridge. They help remove any food particles or plaque that may have accumulated around the abutment teeth (the natural teeth supporting the bridge).
- Antibacterial mouthwash: Regular use of an antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria buildup, prevent gum disease, and maintain good oral hygiene. It’s also important to rinse after meals when you cannot brush immediately.
- Avoid hard foods: Hard foods, such as candy, ice, or nuts, can damage the bridge or cause the abutment teeth to break. Try to avoid chewing on these items to preserve the integrity of your dental bridge.
How Long Can a Dental Bridge Last?
- Typical lifespan: On average, a dental bridge lasts between 5 to 15 years, depending on the material used and how well you care for it. High-quality materials, such as zirconia or metal-ceramic, can offer more durability, while lower-cost materials may require more frequent replacement.
- Factors affecting longevity: The lifespan of a dental bridge depends on several factors, including the condition of the surrounding teeth, the quality of materials, and how well you maintain your oral hygiene. Regular dental checkups are essential to monitor the condition of the bridge and address any issues early.
Can a Dental Bridge Be Removed and Re-cemented?
- Re-cementing option: If a dental bridge becomes loose but remains intact, it is possible for your dentist to remove and re-cement it. However, it’s important to have it checked promptly to avoid further complications, such as tooth decay or gum infection.
- Risks upon removal: There’s a risk of fracture or damage to the bridge when attempting to remove and re-cement it, so it should only be done by a professional. In some cases, a new bridge might be necessary if the old one is too damaged.
Does a Dental Bridge Affect Eating or Speaking?
- Temporary discomfort: After the procedure, you may experience temporary discomfort or a slight lisp while speaking. This is normal as your mouth adjusts to the new bridge.
- Adaptation period: For most patients, the discomfort diminishes within a few days as you get used to the bridge. Eating may initially be uncomfortable, but as you adjust, it should be easier to eat most foods without difficulty.
- Long-term comfort: Over time, a well-fitted dental bridge should function like your natural teeth, allowing you to speak and chew comfortably without noticing much difference.
What Are the Risks and Alternatives to Dental Bridges?

While dental bridges are a great solution for many patients, there are risks and potential disadvantages to consider. Additionally, there are alternative treatments to dental bridges that might better suit certain individuals or specific dental needs.
Is Getting a Dental Bridge Painful?
- Local anesthesia: The procedure for placing a dental bridge is typically done under local anesthesia, which means you will not feel any pain during the procedure itself.
- Post-operative discomfort: After the procedure, some sensitivity or mild discomfort in the treated area is common. This may last a few days but should subside as the mouth heals. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage any discomfort.
- Temporary discomfort: Some patients report feeling a bit of pressure or discomfort while chewing after the bridge is placed, but these symptoms usually go away once the mouth has fully adjusted.
What Are the Disadvantages of a Dental Bridge?
- Reshaping of healthy teeth: One of the main disadvantages of dental bridges is the need to reshape or grind down the healthy teeth (abutments) that support the bridge. This process can weaken the abutment teeth and may increase the risk of future dental issues like decay or fractures.
- No prevention of bone loss: Unlike dental implants, dental bridges do not help preserve jawbone structure. After the loss of a tooth, bone resorption occurs in the empty space, and bridges do not address this concern as implants do.
- Potential for damage: While dental bridges are generally durable, they can break or become loose if subjected to too much force. Chewing hard foods or grinding your teeth could cause damage, especially to the pontic or the crowns.
- Gum irritation: The gums around the bridge may become irritated or inflamed, especially if the bridge doesn’t fit properly or if it’s difficult to clean around it.
What Are Common Problems with Dental Bridges?
- Decay under crowns: One of the most common issues with dental bridges is the development of decay under the crowns or at the gum line of the supporting teeth. If this happens, the bridge may need to be replaced.
- Loose or broken bridges: Over time, a bridge can become loose or break due to the natural wear and tear on the materials. In such cases, the bridge may need to be re-cemented or replaced entirely.
- Gum irritation or recession: If the bridge is not properly fitted, the surrounding gums may become irritated or may begin to recede, exposing the abutment teeth.
What Are the Alternatives to a Dental Bridge?
- Dental implants: Dental implants are one of the most popular and effective alternatives to dental bridges. Implants replace the entire tooth, including the root, and provide a more permanent solution without affecting surrounding healthy teeth. Implants also help preserve jawbone density and prevent bone loss that typically occurs after a tooth extraction.
- Partial dentures: Removable partial dentures are another option, especially for patients who need to replace multiple teeth. Partial dentures are cost-effective and easy to adjust but may not be as comfortable or durable as a fixed bridge or implant.
- Resin-bonded bridges: Often used for front teeth, these Maryland bridges are less invasive and don’t require reshaping the abutment teeth. However, they are less durable than traditional bridges and may not be suitable for molars.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dental Bridge

What is a Dental Bridge?
A dental bridge is a prosthetic device designed to replace one or more missing teeth. It typically consists of two crowns on the adjacent teeth, called abutments, and a false tooth or teeth in the middle, known as pontics. A dental bridge helps fill the gap left by missing teeth, restoring both the appearance and functionality of your smile.
How Long Does a Dental Bridge Last?
The longevity of a dental bridge can vary depending on factors such as the material used, the patient’s oral hygiene, and the condition of the surrounding teeth. On average, a well-maintained dental bridge can last anywhere from 5 to 15 years. Regular checkups with your dentist and practicing good oral hygiene can help extend the life of the bridge.